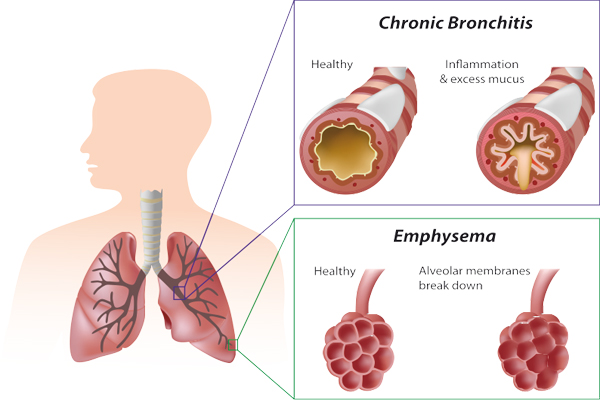
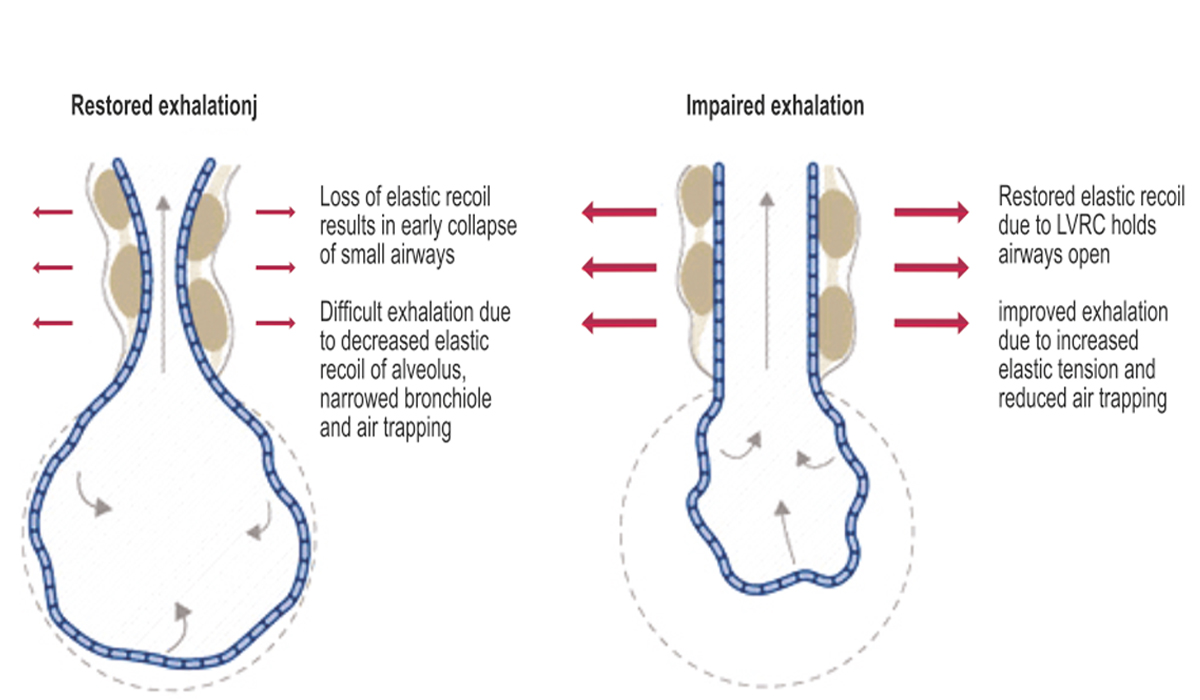
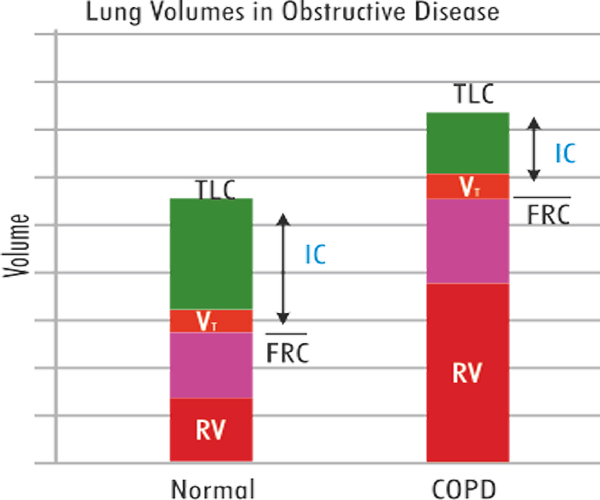
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseasse (COPD)
KEY POINTS
Assess and monitor disease
- Spirometry is gold standard, the presence of a post-bronchod lator FEV1/FVC < 0.70 confirm the presence of persistentairflow imitation
- Measurement of arterial blood gas tensions should be considered in al patients with FEV1 < 40% predicted orcinical signs suggestive of respiratory failure or rightheart failure
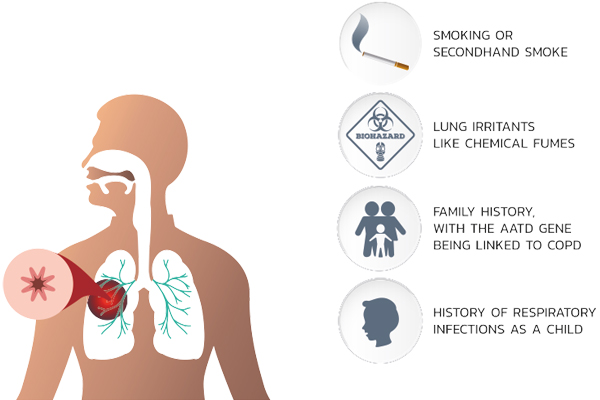
Reduce risk factors
- Reduction of total personal exposure to tobacco smoke, occupational custs and chemicals, and indoor air pollutants are important goals to prevent the onset and progression of COPD.
- Smoking cessation is the single most effective and cost-effective way to reduce the risk of developing COPD and stop its progression
Manage stable COPD
- The overall approach to managing stable COPD should be characterized by a stepwise increase in treatment, depending on the severity of the disease
- Skiing can play a role in improving skills, ability to cope withiness, and health status
- Bronchodilator medications are central to the symptomatic management of COPD. They are given on anes-needed basis or on a regular basis
to prevent or reduce symptoms. - The principal bronchodilator is anticholinergics (SAMA & LAMA), as anticholinergic tone is high in COPD patients
- Combination of different brocholitators are elective LABA&LAMA)
- Regular treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids should only be prescribed for symptomatic patients with COPD with a documented Spirometric response to glucocorticosteroids or for those with an FEV1 <50% predicted and repeated exacerbations requiring treatment with antibiotics or oral steroids
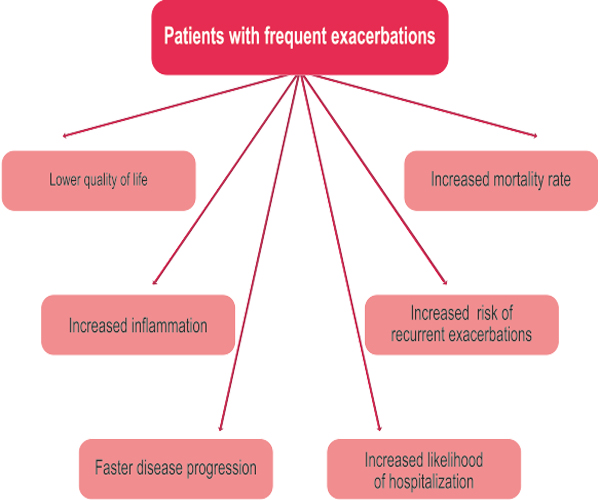
Manage exacerbations
- The most common causes of an exacerbation is arpolution, but the cause of approximately one-third of severe exacerbations cannot be identified
- Inhaled bronchodiators (particularly beta 2-agonists or anicholinergics)theophyline, and oral, glucocorticosteroids are efective treatment of acute Bracertations of COPD
- Patients experiencing COPD exacerbations with clinical signs of airway infection 18.9., increased volume and change of color of sputum, orfever may benefit from antibiotic treatment
- Nonimasive posive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) in acute exacerbations improves blood gases and pH, reduces in hospital mortality.decreases the need for invasive mechanical ventistion
Pulmonary rehabilitation
- COPD patients benefit from early structured pulmonary rehabilitation program
- A good nutrition programmustforal COPD patients
- The long-term administration of anygen >16 h per day to patients with chronic respiratory failure has been shown to increase survival
- All stable hypercapnic COPD patients benefit by long term noninvasive ventilation
- Ruand pneumococcal vaccinations are beneficial to prevent exacerbation
Comorbidity assessment and treatment
- Treat the disease as whole notas hole in the body

